Check Out How Big Is The Moon Compared To The eEarth & 12 Facts
Check Out How Big Is The Moon Compared To The eEarth & 12 Facts
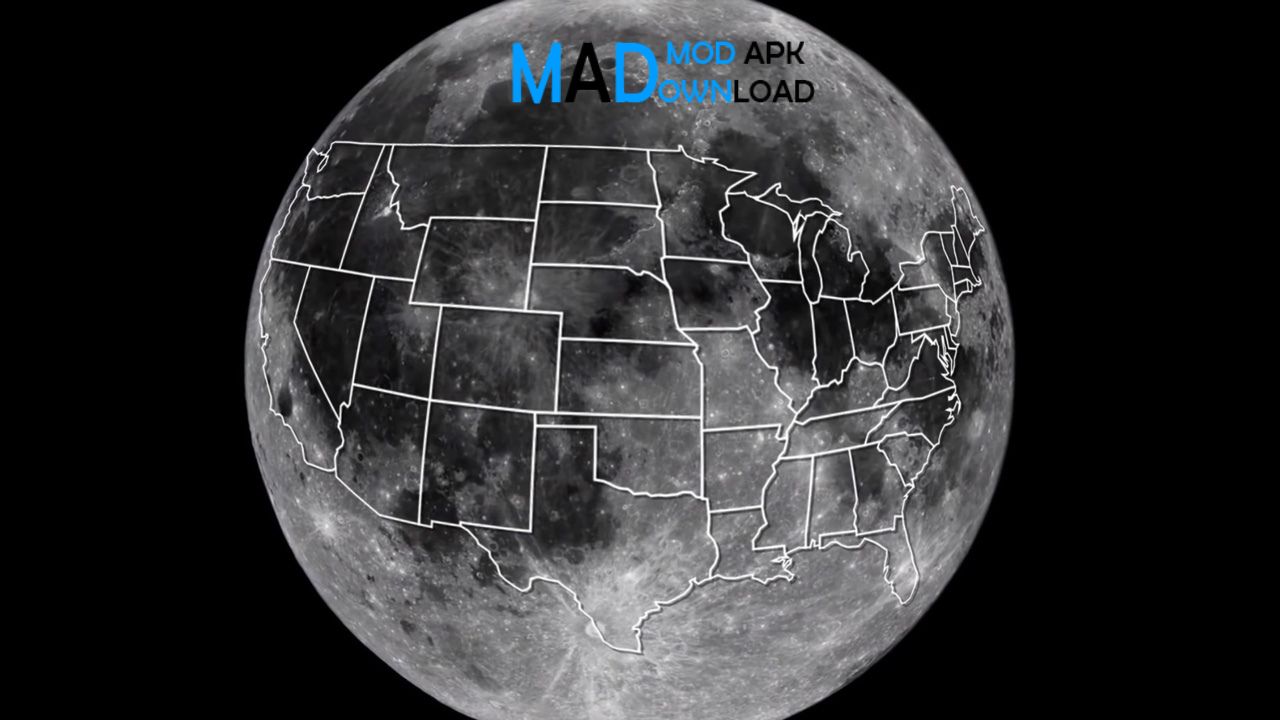
In the night sky, the moon appears to be the largest celestial body. Depending on where it is in respect to the earth, the moon takes on different shapes. The earth and moon are very different from one another as astral bodies. That is why the question of How big is the moon compared to the earth comes to mind. In this write-up, we will clear your doubts on that and will also discuss amazing facts about the Moon .
Comparing Moon To Earth
To know how big is the moon compared to the earth, there are several factors we have to consider. They are-
1.Diameter And Radius
According to NASA, the moon’s breadth is less than one third of Earth’s breadth. The average diameter and radius of the moon are 2,159.2 miles (3,475 km) and 1,079.6 miles (1,737.5 km), respectively. Moon has a circumference of 6,783.5 miles, which roughly converts to 10,917 km.
2.Surface Area
Moon’s 37.9 million square kilometres of surface area. If you think it’s large, it’s not. For comparison let’s take Asia’s surface area which covers 44.4 million square kilometres. Earth’s total surface area is more than 500 million sq. kilometres. From that we can say that the Moon is only seven percent of the Earth’s total surface area. So if you are wondering how big is the moon compared to the earth, it’s actually very small.
3.Volume
The moon has a 21.9 billion cubic kilometres volume. That seems like a massive amount, but the Earth’s volume is almost 1 trillion cubic kilometres. So, the Moon’s volume is just 2% of that of the Earth.
4.Mass
When it comes to mass, the Moon weighs 7.347 x 1022 kg in weight. However, the Earth is significantly bigger and has a mass of 5.97 x 1024 kg. This proves that the Moon’s mass is only 1.2% of the Earth’s mass. Earth is 81 times heavier than the Moon.
Amazing Facts About Moon
Now that you know how big is the moon compared to the earth, let’s have a look at some of the amazing facts about the moon.
1.Lunar Origins
The Giant Impact Hypothesis is the most popular explanation for how the Moon was formed. This hypothesis states that a Mars-sized celestial body struck the early Earth 4.5 billion years ago, ejecting debris that later consolidated to form the Moon.
2.Tidal Forces
Moon’s gravitational force causes the tides on the oceans of earth. High tides are brought on by a bulge in the Earth’s seas brought on by the Moon’s gravitational pull during its orbit. Due to centrifugal force, the side opposite the Moon sees a second high tide, while the regions in between experience low tides.
3.Celestial Dance
The orbital dance between the Moon and Earth is known as the celestial dance. The Moon completes one complete circle around our planet in around 27.3 days. However, it takes the Moon approximately 29.5 days to go through its entire cycle of phases, from New Moon to Full Moon and back, due to Earth’s orbit around the Sun.
4.Lunar Maria
The lunar maria (plural: mare) are enormous, dark, flat plains on the surface of the moon. Basaltic lava flows, which make up the majority of these locations, are what give them their ominous appearance. The maria, which are visible from Earth with the naked eye, were created by volcanic activity that happened previously.
5. Moon’s Actual Shape Is Oval
The Moon is actually formed like an egg and isn’t exactly round as it appears to be. The Moon has an apparent egg shape because its centre of mass is around 1.2 miles from its geometric centre. It also changes its shape frequently which raises the question how big is the moon compared to the earth.
6.Impact Craters
Countless impact craters dot the Moon’s surface, bearing witness to the continuous assault of meteoroids and asteroids over billions of years. Since the Moon doesn’t experience erosion or tectonic activity like Earth does, these old impact structures have been preserved.
7.Moonquakes
The Moon experiences seismic activity, or moonquakes, as a result of the interior of the Moon cooling and contracting as well as the gravitational pull of Earth. Moonquakes have unique causes and characteristics unlike those of the Earth.
8.Lunar Regolith
A layer of loose, broken debris known as regolith covers the Moon’s surface. This layer is the product of thousands of years’ worth of meteorite impacts disintegrating rocks into tiny particles. For lunar exploration, the regolith can reach several metres deep in some places.
9.Extreme Temperature Fluctuations
Extreme temperature fluctuations are experienced on the Moon because it lacks a substantial atmosphere to hold heat in. Temperatures on the moon can reach above 100 degrees Celsius (212 degrees Fahrenheit) during the day and around 150 degrees Celsius (-238 degrees Fahrenheit) at night.
10.Water Ice Finding
In recent years, researchers have found evidence of water ice on the Moon, primarily in areas that are constantly shaded at the lunar poles. Given that water is an important resource for potential human missions, this discovery has opened a new window for research.
11.Dark Parts Of Moon Are Actually Lava
About 16 percent of the Moon’s surface is covered in flat, dark layers of basaltic lava flows. It is believed that the lava travelled great distances before engulfing low-lying regions like impact basins. However, because of factors like erosion from items striking the moon or fresher flows covering older ones, it is challenging to pinpoint where the lava originally erupted from.
12.Unsolved Moon Mysteries
As there are some questions like how big is the moon compared to the earth that is known to us, there are also many unsolved mysteries about the Moon. The origin of several minerals found on the Moon that differ from those on Earth is one such unsolved question.